To ensure optimal performance and longevity of power transformers, routine maintenance and systematic inspections are critical. This guide outlines essential practices for transformer maintenance, integrating industry standards and modern monitoring technologies.
1.Key Components of Routine Transformer Maintenance
Regular inspection of core components helps prevent failures and ensures compliance with safety regulations:
- Oil Level and Quality Checks: Monitor insulating oil levels and test for contaminants like moisture or dissolved gases
- Temperature Monitoring: Track winding and oil temperatures using sensors; abnormal rises may indicate overload or insulation degradation.
- Winding Insulation Testing: Perform dielectric strength tests to assess insulation integrity.
- Cooling System Inspection: Clean radiators and fans to maintain efficient heat dissipation.
2.Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
Modern technologies enhance traditional inspection methods:
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Detects early signs of internal faults by analyzing gases in transformer oil.
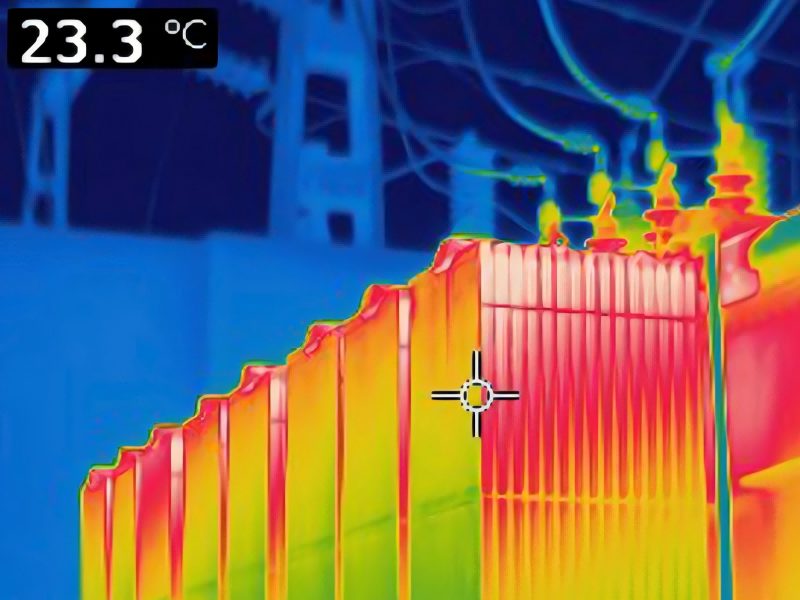
- Thermal Imaging: Identifies hotspots in bushings or connections that may signal impending failures.
- Remote Monitoring Systems: Web-based platforms enable real-time tracking of parameters like load, temperature, and oil condition.
3.Best Practices for Preventive Maintenance
Adopt a structured approach to minimize downtime:
- Scheduled Inspections: Conduct biannual visual checks and annual comprehensive tests.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of all inspections, tests, and repairs for compliance and trend analysis.
- Staff Training: Ensure technicians are proficient in using diagnostic tools and interpreting results.





